How to Develop and Debug Java Applications on Kubernetes

Kubernetes is an open-source project for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containers. It has rapidly become the standard to run production workloads and the community around it is just great!
But developing in Kubernetes presents some challenges. The typical development workflow looks like this: write code, build a Docker image, push it to the registry, redeploy, validate your changes, rinse and repeat. This flow is not only slow, but it also prevents us from benefiting from standard features of Java tools such as fast incremental builds, automatic hot reloads or powerful debuggers.
Okteto was created to solve this problem. On this blog post, we will show you how Okteto improves the developer experience in Kubernetes for Java developers. You will be able to take full advantage of tools like Maven, Gradle, dependency caching, popular frameworks hot reloads (Spring Boot, Quarkus, Micronaut, ...) or IDE debuggers (Eclipse, IntelliJ, VS Code, ...) while developing your application directly in Kubernetes.
Step 1: Deploy the Java Sample App
Get a local version of the Java Sample App by executing the following commands:
Maven
$ git clone https://github.com/okteto/java-maven-getting-started
$ cd java-maven-getting-started
Gradle
$ git clone https://github.com/okteto/java-gradle-getting-started
$ cd java-gradle-getting-started
The k8s.yml file contains the Kubernetes manifests to deploy the Java Sample App. Run the application by executing:
You can deploy to your own Kubernetes cluster or give Okteto Cloud a try. Okteto Cloud is a development platform for Kubernetes applications. Sign up today to get a free developer account with 4 CPUs and 8GB of RAM.
$ kubectl apply -f k8s.yml
deployment.apps "hello-world" created
service "hello-world" created
This is cool! You typed one command and a dev version of your application just runs 😎.
Step 2: Install the Okteto CLI
The Okteto CLI is an open-source project that lets you develop your applications directly in Kubernetes while taking advantage of well-known local tooling . We will use it to speed up our development cycle instead of using the typical development workflow based on building docker images and redeploying containers.
Install the Okteto CLI >= 1.9.0:
MacOS / Linux
$ curl https://get.okteto.com -sSfL | sh
Windows
Download https://downloads.okteto.com/cli/okteto.exe and add it to your $PATH.
Step 3: Create your okteto manifest
To start developing on the Java Sample App you first need to create an okteto manifest. With the Java Sample App deployed, run the following command to create your okteto manifest:
$ okteto init
This command walks you through creating an okteto manifest.
It only covers the most common items, and tries to guess sensible defaults.
See https://okteto.com/docs/reference/manifest for the official documentation about the okteto manifest.
Use the arrow keys to navigate: ↓ ↑ → ←
Select the deployment you want to develop:
▸ hello-world
Use default values
The okteto init command will scan the available deployments in your Kubernetes namespace and ask you to pick one.
Select the hello-world deployment. It's the one we deployed on the previous step.
✓ hello-world
✓ Deployment 'hello-world' successfully analyzed
✓ okteto manifest (okteto.yml) created
i Run 'okteto up' to activate your development container
The okteto init command creates the following okteto.yml file:
Maven
name: hello-world
image: okteto/maven:3
command: bash
volumes:
- /root/.m2
sync:
- .:/usr/src/app
forward:
- 8080:8080
- 5005:5005
Gradle
name: hello-world
image: okteto/gradle:6.5
command: bash
volumes:
- /home/gradle/.gradle
sync:
- .:/usr/src/app
forward:
- 8080:8080
- 5005:5005
This file defines how to activate a development container for the Java Sample App:
name: the name of the Kubernetes deployment you want to put on development mode.image: the image used by the development container. More information on development images here.command: the start command of the development container.volumes: a list of paths in your development container to be mounted as persistent volumes. This is useful to persist the maven/gradle caches.sync: the folders that will be synchronized between your local machine and the development container.forward: a list of ports to forward from your development container.
Also, the okteto init command creates a .stignore file to indicate which files shouldn't be synchronized to your development container.
This is useful to avoid synchronizing binaries, build artifacts or git metadata.
Step 4: Activate your development container
Next, execute the following command to activate your development container:
$ okteto up
✓ Development container activated
✓ Files synchronized
Namespace: default
Name: hello-world
Forward: 8080 -> 8080
5005 -> 5005
Welcome to your development container. Happy coding!
default:hello-world app>
Working in your development container is the same as working on your local machine. Start the application by running the following command:
Maven
default:hello-world app> mvn spring-boot:run
Gradle
default:hello-world app> gradle bootRun
The first time you run the application, Maven/Gradle will compile your application. Wait for this process to finish.
Okteto automatically forwards port 8080 from your local computer to the development container, making it accessible via localhost. Test your application by running the command below in a local shell:
$ curl localhost:8080
Hello world!
Step 5: Develop directly on Kubernetes
Open src/main/java/com/okteto/helloworld/RestHelloWorld.java in your favorite local IDE and modify the response message on line 11 to be Hello world from the cluster!. Save your changes.
package com.okteto.helloworld;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class RestHelloWorld {
@GetMapping("/")
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello world from the cluster!";
}
}
Your IDE will auto compile only the necessary *.class files that will be synchronized by Okteto to your application in Kubernetes. Take a look at the development container shell and notice how the changes are detected by Spring Boot and automatically hot reloaded. To enable Spring Boot hot reloads you need to import the spring-boot-devtools dependency in your application:
Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
Gradle
dependencies {
...
dev("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools")
...
}
Call your application to validate the changes:
$ curl localhost:8080
Hello world from the cluster!
Cool! Your code changes were instantly applied to Kubernetes. No commit, build or push required 😎!
Step 6: Debug directly in Kubernetes
Okteto enables you to debug your applications directly from your favorite IDE. Let's take a look at how that works in Eclipse, one of the most popular IDEs for Java development. To enable debug mode, define the following JVM arguments in your Gradle/Maven configuration files:
Maven
<configuration>
<jvmArguments>
-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005
</jvmArguments>
</configuration>
Gradle
bootRun {
jvmArgs = ["-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005"]
...
}
Open the Debug configuration dialog, add a new Remote Java Application debug configuration, and point it to localhost:5005:
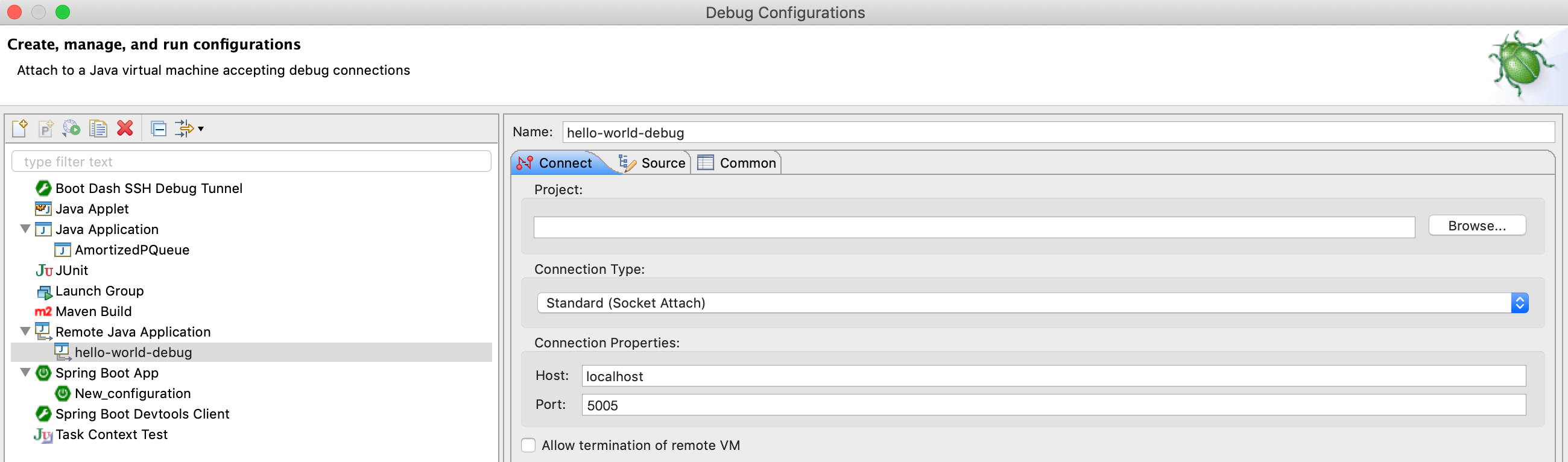
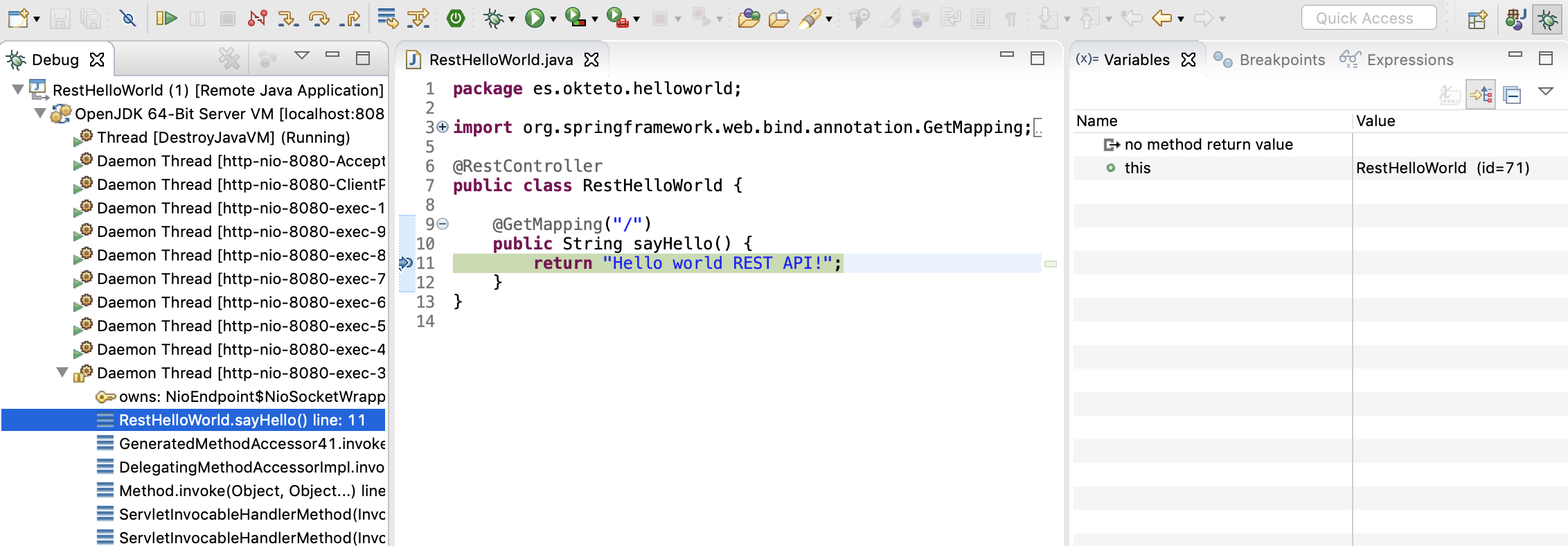
Click the Debug button to start a debugging session. Add a breakpoint on src/main/java/es/okteto/helloworld/RestHelloWorld.java, line 11, and call your application by running the command below from your local shell.
$ curl localhost:8080
The execution will halt at your breakpoint. You can then inspect the request, the available variables, etc...
Conclusions
Kubernetes has the potential to be a great development platform, providing replicable, resource-efficient and production-like development environments. We have shown you how to use Okteto to create a development workflow that also lets you take advantage of features like incremental builds, debuggers or hot reloads while developing your application directly on Kubernetes.
Visit our website to know more about how to improve your team developer productivity with Okteto. Follow us on Twitter and join our #okteto channel in the Kubernetes community Slack to share your feedback with our community.


 Arsh Sharma
Arsh Sharma